C02 Predictive coding for anxiety control: hierarchical network in the primate cognitive-limbic system.
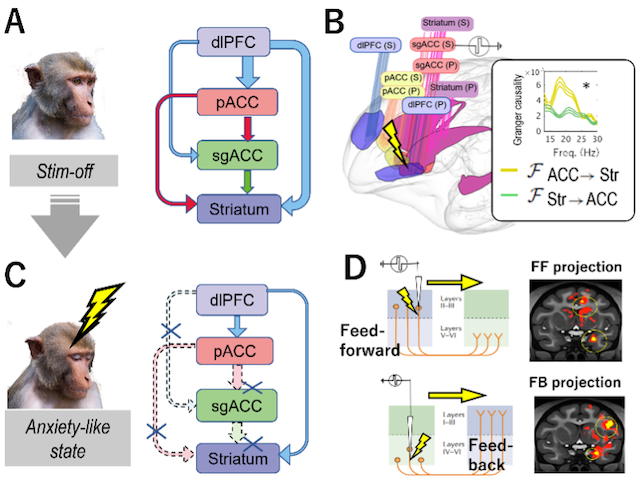
Interareal interaction of the large-scale brain network of primates has been examined using a computational model known as “predictive coding,” focusing on the interaction between cognitive and visual areas. Granger causality in neural oscillatory signals between these regions reveals a correlation with anatomical hierarchy, which classifies projections from superficial layers as feed-forward (FF) and those from deep layers as feedback (FB). Neural oscillations within gamma and beta ranges demonstrate directional patterns along this hierarchy, aligning with the neural mechanisms of predictive coding. Our study aims to investigate whether the hierarchical principles proposed by predictive coding can extend to interactions between cognitive and limbic areas. To address this question, we have trained macaques on conflict tasks to quantify anxiety and simultaneously recorded local field potentials (LFP) from various regions of the cognitive and limbic cortices, and striatum during task performance (Figure A). Utilizing network analysis techniques such as Granger causality and spike-triggered LFP, we aim to elucidate the directionality of the large-scale brain network (Figure B). We will perform electrical microstimulation (EM) during LFP recording to reveal changes in network interactions when it induces anxiety-like states. We then elucidate the pathological features of depression and anxiety (Figure C). Finally, by selectively stimulating the deep and superficial layers of the limbic cortices, we aim to identify the FF and FB pathways in the network by mapping stimulation-induced activity using fMRI. These efforts will contribute to a deeper understanding of the hierarchical structure of the anxiety network (Figure D).

Principal investigator: Kenichi Amemori
Program-specific Associate Professor, Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology (ASHBi), Kyoto University
